
The operating system is in charge of storing and accessing files. Network virtualization, replication, mirroring, security, compression, deduplication, traffic analysis, process automation, storage provisioning, and memory management are some of the features that may be included. Storage management is a procedure that allows users to maximize the utilization of storage devices while also protecting data integrity on whatever media on which it lives. Keeps records of the status and locations of files.The files on a system are stored in different directories. These groupings of resources are referred to as file systems. It also keeps track of information, location, uses, status, and so on. It specifies which process receives the file and for how long. The operating system manages resource allocation and de-allocation. Decides which process can use which device for how much time.Allocates and deallocates devices to different processes.The processes may require devices for their use. Increasing the efficiency of the system.Īn operating system regulates device connection using drivers.Hence, the OS makes sure that the devices get fair processor time. Since every device should get a chance to use the processor.Therefore, the OS makes sure that the CPU should be as busy as possible. Since the proper utilization of the CPU is necessary. The purpose of CPU scheduling is as follows: Allocates and deallocates processor to the processes.Ĭertain algorithms used for CPU scheduling are as follows:.When more than one process runs on the system the OS decides how and when a process will use the CPU. The operating system determines the status of the processor and processes, selects a job and its processor, allocates the processor to the process, and de-allocates the processor after the process is completed. Processor management is an execution unit in which a program operates.
#Typesy os software#
In multiprogramming, the operating system selects which processes acquire memory when and how much memory they get.Įvery software that runs on a computer, whether in the background or in the frontend, is a process.Distributes the memory while multiprocessing.Keeps a record of which part of primary memory is used by whom and how much.Hence, it is required to manage the memory. Therefore, there can be more than one program present at a time. When the program is completed, the memory region is released and can be used by other programs.
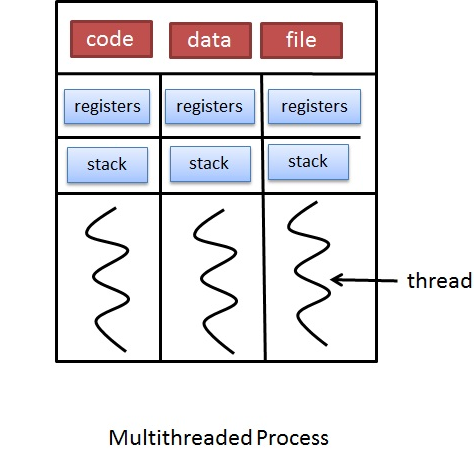
Main memory is a quick storage area that may be accessed directly by the CPU. Whatever program is executed, it has to be present in the main memory. It is the management of the main or primary memory.
Operating systems enable users to get started on the things they wish to complete quickly without having to cope with the stress of first configuring the system. Convenience – An operating system improves the use of a machine.The primary goals of an operating system are as follows:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
